Plastic Rapid Prototyping: Revolutionizing Metal Fabrication
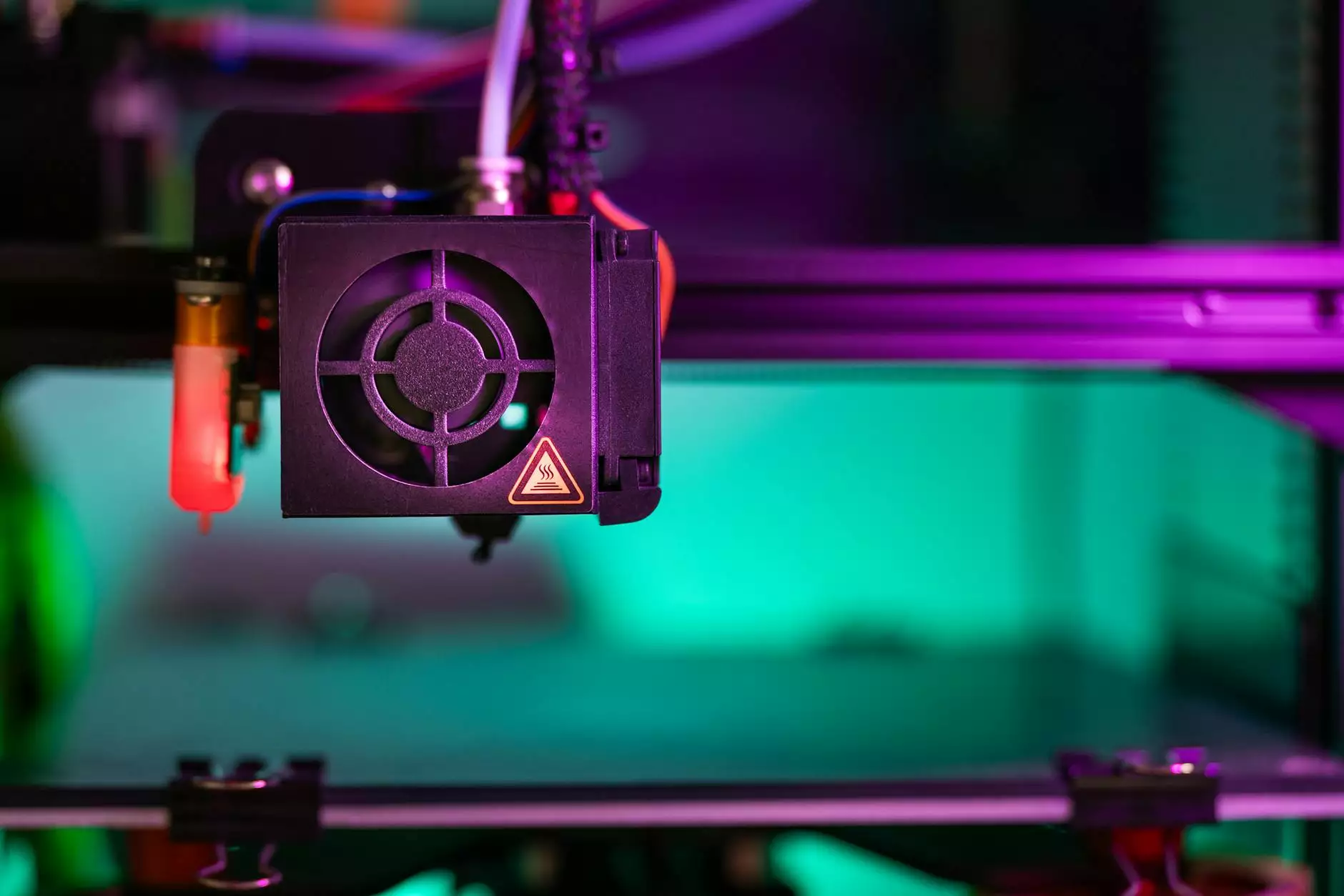

Understanding Plastic Rapid Prototyping
Plastic rapid prototyping refers to a process that allows the quick fabrication of physical parts using three-dimensional (3D) computer-aided design (CAD) data. This innovative technology has become a cornerstone in various industries, particularly in metal fabrication. It enables engineers and designers to create models that are not only functional but also aesthetically pleasing, expediting the design process considerably.
The Importance of Prototyping in Metal Fabrication
In the realm of manufacturing, especially in the metal fabrication sector, the importance of prototyping cannot be overstated. Here are several reasons why:
- Enhanced Design Accuracy: Prototypes allow for validation of designs before full-scale production.
- Cost-Effective Adjustments: Making changes during the prototyping phase is significantly less expensive than during manufacturing.
- Time Efficiency: Rapid prototyping reduces the time from concept to production.
- Increased Collaboration: Prototypes facilitate better communication among team members and stakeholders.
How Plastic Rapid Prototyping Works
The process of plastic rapid prototyping typically involves the following steps:
- Design: The concept is turned into a 3D CAD model.
- Slicing: The CAD model is sliced into thin horizontal layers using software.
- Printing: The printer deposits plastic layer by layer based on the sliced design.
- Post-Processing: The prototype undergoes finishing touches such as sanding or painting.
This method enhances the prototyping speed, allowing businesses to achieve functional prototypes within days rather than weeks or months.
Advantages of Using Plastic in Rapid Prototyping
Using plastic for rapid prototyping comes with significant advantages that benefit the metal fabrication industry:
- Lightweight and Durable: Plastic materials can simulate the weight and durability of metal, making them ideal for testing.
- High Flexibility: Plastics can be manipulated into various shapes and sizes, providing design flexibility.
- Low Cost: Plastic prototypes are cheaper to produce than metal prototypes, allowing for more iterations on design.
- Speed: The production process for plastic prototypes is significantly faster, facilitating quicker testing and iteration.
Applications of Plastic Rapid Prototyping in Metal Fabrication
Plastic rapid prototyping serves a myriad of applications within the metal fabrication industry:
- Tooling: Creating molds and tool designs that are tested in plastic before metal manufacturing.
- Part Design: Prototyping parts that will eventually be fabricated in metal to assess fit and function.
- Packaging Solutions: Designing and testing packaging components from plastic, which can be easily altered before final production.
- End-Use Products: Developing consumer products that require validation in form and function before metal production begins.
Challenges and Considerations in Plastic Rapid Prototyping
While there are numerous benefits to plastic rapid prototyping, businesses also face some challenges:
- Material Limitations: Not all plastic materials behave like metals, which can affect simulation accuracy.
- Surface Finish: Plastic prototypes may require additional finishing processes to achieve desired aesthetics.
- Scaling Issues: Prototypes may not always scale perfectly to metal parts, necessitating additional adjustments after prototyping.
- Technical Expertise: A lack of trained personnel in operating advanced prototyping equipment can hinder efficiency.
The Future of Plastic Rapid Prototyping in Metal Fabrication
The integration of plastic rapid prototyping techniques into metal fabrication is set to evolve significantly, propelled by technological innovations:
- Advanced Materials: The development of new plastic materials that can better mimic the strengths of metals.
- Hybrid Prototyping Techniques: Combining traditional and rapid prototyping methods for enhanced efficiency.
- Automation and AI: Utilizing artificial intelligence to optimize the prototyping process, reducing time and cost.
- Enhanced Software: Improvements in design software that allow even greater ease in creating complex prototypes.
Conclusion: Embracing the Change in Metal Fabrication
The world of metal fabrication is undergoing a transformation thanks to the capabilities of plastic rapid prototyping. Companies that embrace these innovations stand to gain a competitive advantage through enhanced efficiency, reduced costs, and improved product quality. As technology continues to advance, the relationship between plastic prototyping and metal production will undoubtedly strengthen, paving the way for a new era of manufacturing excellence.