Understanding CT Scans for Lung Cancer Diagnosis and Management

Lung cancer remains one of the leading causes of cancer-related deaths across the globe. Accurate diagnosis and effective treatment are critical for improving survival rates among patients. One of the most effective diagnostic tools available today is the CT scan for lung cancer. This article delves into the significance of CT scans in the realm of lung cancer, discussing how they work, what to expect during the procedure, and their benefits in treatment planning.
What is a CT Scan?
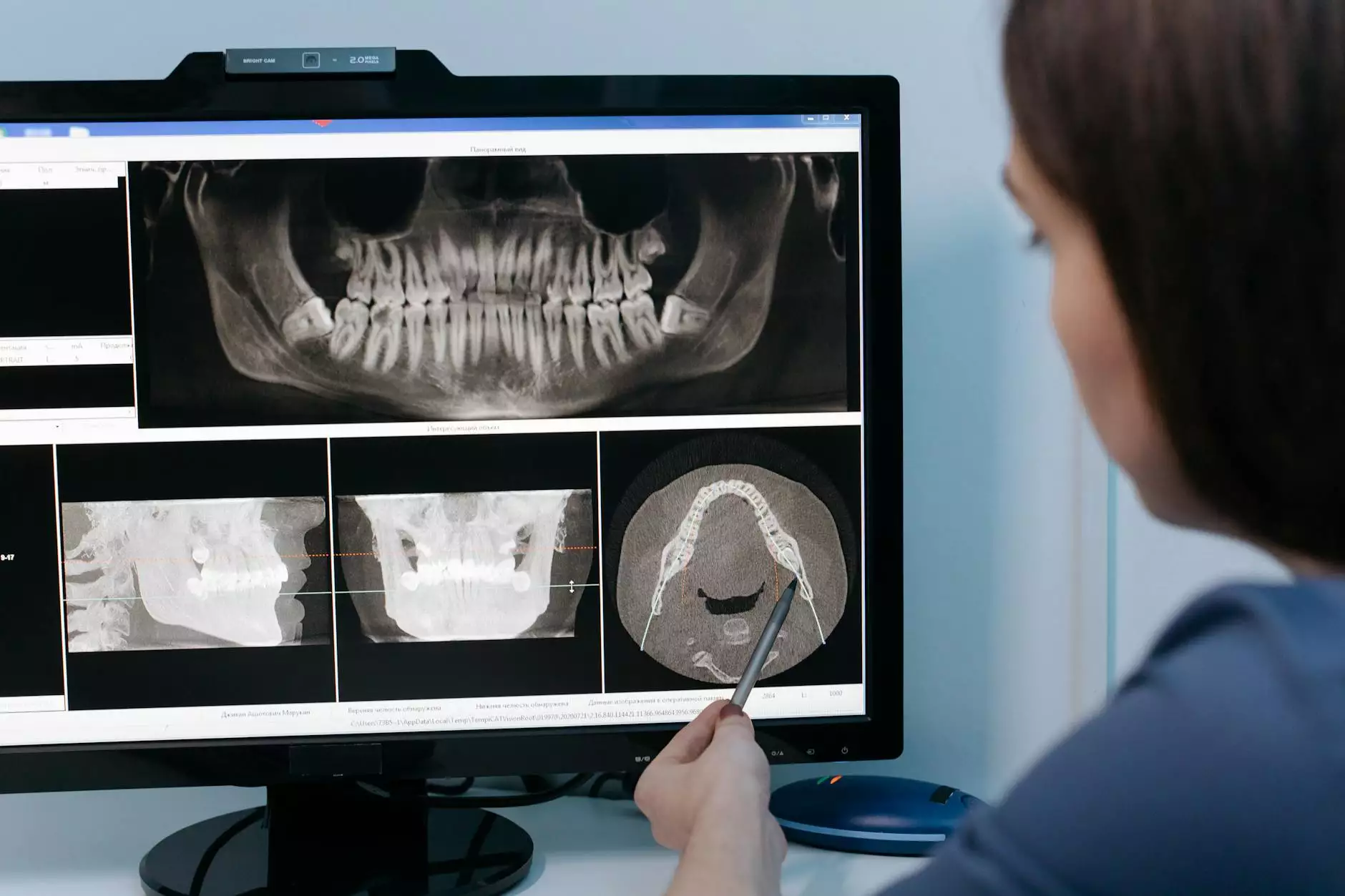
A CT scan, or computed tomography scan, combines a series of X-ray images taken from different angles and uses computer processing to create cross-sectional images of bones, blood vessels, and soft tissues inside the body. This imaging technique is pivotal in the detection, diagnosis, and treatment of various medical conditions, including lung cancer.
Why are CT Scans Important in Diagnosing Lung Cancer?
Early detection of lung cancer significantly influences treatment success and patient prognosis. Here are some key reasons why CT scans are crucial in this context:
- High Sensitivity: CT scans are known for their high sensitivity in detecting pulmonary nodules and masses that may represent early-stage lung cancer.
- Three-Dimensional Imaging: The ability to visualize internal structures in three dimensions allows for a thorough assessment of the lungs and surrounding tissues.
- Monitoring Disease Progression: CT scans can be used to monitor the size and growth of tumors, essential for evaluating treatment efficacy.
- Guiding Biopsies: They can help in guiding needle biopsies to obtain tissue samples for definitive diagnosis.
How Does a CT Scan Work?
During a CT scan, the patient lies flat on a table that slides into the CT scanner, which is a large, doughnut-shaped machine. The procedure is painless and typically lasts about 30 minutes. Here’s what happens during the scan:
- The patient is positioned correctly to ensure the lungs are optimally visualized.
- A contrast material may be administered via IV to enhance the visibility of certain structures during the scan.
- The scanner rotates around the body, capturing detailed images from various angles.
- Computer software processes these images to create detailed cross-sectional views of the lungs.
What to Expect During a CT Scan for Lung Cancer
Understanding what to expect during a CT scan can help alleviate any anxiety associated with the procedure. Here are the steps involved:
Preparation
Prior to the scan, patients may need to:
- Discuss any medical conditions and medications with their healthcare provider.
- Follow specific dietary restrictions if a contrast agent is required.
During the Scan
While the scan is being conducted:
- It is important for patients to remain as still as possible to avoid blurring the images.
- Patients will hear buzzing or clicking sounds from the machine as it operates.
- Breathing instructions may be given, such as holding one’s breath for short periods.
After the Scan
Generally, patients can resume normal activities immediately following the scan, unless advised otherwise. If a contrast dye was used, it will be monitored for any allergic reactions.
Interpreting CT Scan Results
After a CT scan is completed, a radiologist analyzes the images and prepares a report. This report is sent to the referring physician, who will discuss the findings with the patient. Important aspects of the results include:
- Nodule Size and Shape: The characteristics of any detected nodules can indicate whether they are benign or malignant.
- Presence of Metastasis: CT scans can reveal if lung cancer has spread to other parts of the body.
- Response to Treatment: Changes in the size of known tumors can help determine if the current treatment is effective.
Benefits of CT Scans in Lung Cancer Management
Utilizing CT scans in lung cancer care offers several advantages that enhance patient outcomes:
- Early Detection: Identifying lung cancer early allows for timely intervention, which is crucial for successful treatment.
- Non-invasive: CT scans are typically non-invasive, making them safer compared to surgical biopsies.
- Real-time Monitoring: Lung cancer patients benefit from the ability to track tumor response to ongoing treatments in real-time.
- Comprehensive Assessment: CT scans provide detailed information regarding tumor staging and the involvement of surrounding structures, facilitating informed treatment decisions.
Risks and Considerations of CT Scans
Though beneficial, it is essential to recognize potential risks associated with CT scans:
- Radiation Exposure: CT scans involve exposure to ionizing radiation, although the risks are commonly outweighed by the benefits.
- Allergic Reactions: Some patients may have allergic reactions to contrast materials used during the scan.
Conclusion
The CT scan for lung cancer serves as an indispensable tool in the diagnosis and management of this complex disease. By enabling early detection, precise tumor characterization, and effective monitoring, CT imaging significantly contributes to the planning and implementation of targeted treatment strategies. If you or a loved one are at risk for lung cancer or are experiencing respiratory symptoms, consult your healthcare provider to discuss the potential benefits of a CT scan.
Further Resources
To learn more about lung cancer and its management, consider visiting reputable medical websites or consulting with a healthcare professional. Here are some valuable resources:
- American Cancer Society
- Lung Association
- National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute
Understanding lung cancer and the role of diagnostic tools like CT scans empower patients to take charge of their health journey. Awareness leads to early intervention, better treatment options, and ultimately improved outcomes.